Recently, there has been a boom of information regarding cryptocurrency, blockchain, and other related functions based on Web3.
Not just young users, the government is also starting to understand this new domain of the internet and frame policies accordingly to evolve with the changing world.Â
Many users, developers, and even experts are still trying to grasp and use the constantly updating and transforming sphere of Web3. At such a time, it is necessary to understand the basic framework.
The Internet’s popular world has evolved according to its time and need. The first generation of the World Wide Web- Web1, was launched in 1989.
Tim Berners-Lee, a British scientist, established the Web to conceive and develop the demand for automated information sharing between scientists worldwide in different universities and institutes.
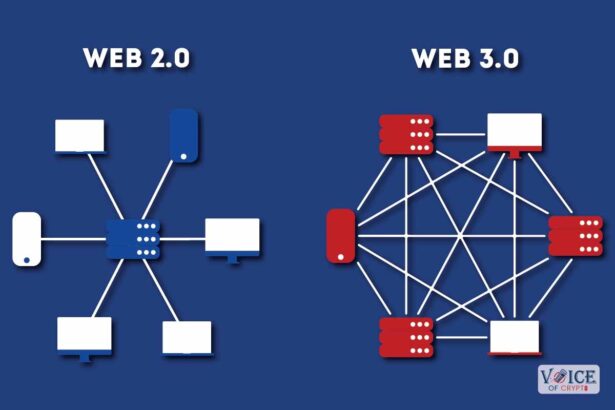
Web3 vs Web2
Under this, people could use the Internet to search for information but only view the pages. Thus, being called “Read Only Web”. The Web was static, with no interactions between providers and users.Â
Replacing the era of the ‘view-restricted’ web, the concept of the second generation of the World Wide Web- Web2- was launched by Dale Dougherty and O’Reilly VP in 2004. Web 2 is more people-centric and participative, with the ability to read/write.
Due to its untraditional model, it is also called as wisdom Web. Under this model, most web page developers had the opportunity to update the information independently.
The information began flowing in all directions. Content providers, advertisers, and viewers could interact with each other for any information or purchase.Â
The two-way interaction gave way to the explosion of social media interaction, blogging, video sharing, chatting, web applications, podcasts, emails, Internet messaging, picture sharing, seminars, online education and all other unimaginable ontologies. The World Wide Web became parallel to the real world.Â
With time the existing model of Web2 was not replaced but extended to the creation of the semantic Web- also known as the third generation of the World Wide Web or Web3.Â
It added machine readability as the key feature to the web documents with the major control to the users. This was, again, created by Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of WWW.
The semantic Web is a new efficient way to represent data on the Web by globally linked machines and databases. The data is accessible and readable by the machines or systems.
It is fundamentally a decentralized, permissionless ecosystem that transfers control from a centralized entity to a pool of users or participants. This decentralized nature is the biggest difference between Web2 and Web3.Â
How Web3 Will Make a Difference?
The main aim of the Web3 architecture is to withdraw the undue advantage from Big Tech or the government controlling the entire internet space and decentralizing it to boost transparency, innovations and online interaction.
It uses Interplanetary File Systems as a method to enhance communication. The semantic Web will also reduce human efforts to search for products or services.Â
Web3 is a solution to some of the main issues posed by Web2, like Data ownership. The Internet is a hub of social media websites.
Still, the P2P economy has brought everything under its control, dictating the users and tracking their content with no concept of privacy and transparency.
Web3, with its decentralized nature, puts greater control in the hands of users aiming to end the monopoly or dictate of a few tech firms. The computing power and decision making is diversified, making the entire system more stable than Web2.Â
Connected to the owner is the issue of privacy and security of data. The data collected by the firms without the concept of complete privacy in Web2 can be leaked.
This makes the user vulnerable to the entire system. Data stored in a centralized database is vulnerable.
As all the big firms and companies are going digital, the data collected for marketing or information purposes is at a higher risk of attacks by hackers.
To solve this, the transparency of the entire process keeps the shared data security intact, de-eliminating the compromise of privacy.Â
Another major solution is given to the issue of government censorship. In the last few years, we have seen an increasing control of the government and its policies in content generation, distribution and consumption on the Internet.
Everything is curbed with the new set of regulations, from artistic or creative to political freedom.
To ensure protection from unfair censorship, web3’s decentralized nature can help where every user can be protected. Moreover, any decision regarding the policy change or execution is made by active participation and the vote of people involved in the project.Â
Lastly, in Web 2, audiences do not have any property rights over consumed content. When you consume information, you only have the emotional or intellectual benefit.
But, you can invest in the Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) introduced under Web3 to provide tangible value to any interaction or consumption. This is like subscribers but only with other rewards. This is very useful for the creator’s economy. Â
Web3 is now being adopted highly by businesses and companies as its benefits overshadow its vices. Its easier onboarding process, accessibility, customized nature and artificial intelligence make the entire prospect attractive for the firms and users.
Additionally, there is also an added advantage of better customer engagement, meeting the expectations of almost everyone.Â
Web3 may not replace the existing internet ecosystem, but it can solve the challenges and extend the uses to that platform. With proper understanding and usage, it is the future of the Internet- An age of prosumers.









I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.